| Wind Watch is a registered educational charity, founded in 2005. |
The wind-energy myth
Credit: By Robert Bryce, National Review Online, www.nationalreview.com 12 August 2011 ~~
Translate: FROM English | TO English
Translate: FROM English | TO English
Hot? Don’t count on wind energy to cool you down. That’s the lesson emerging from the stifling heat wave that’s hammering Texas.
Over the past week or so, Texans have been consuming record-breaking quantities of electricity, and ERCOT, the state’s grid operator, has warned of rolling blackouts if customers don’t reduce their consumption.
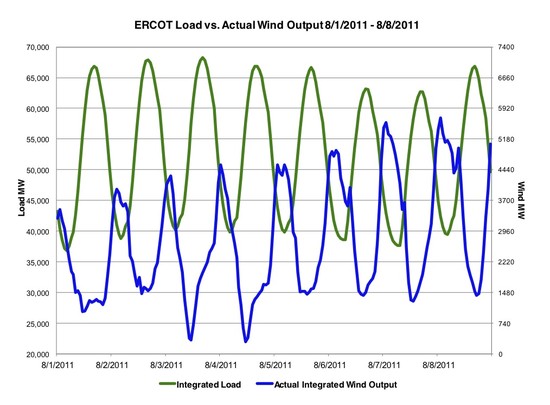
Texas has 10,135 megawatts of installed wind-generation capacity. That’s nearly three times as much as any other state. But during three sweltering days last week, when the state set new records for electricity demand, the state’s vast herd of turbines proved incapable of producing any serious amount of power.
Consider the afternoon of August 2, when electricity demand hit 67,929 megawatts. Although electricity demand and prices were peaking, output from the state’s wind turbines was just 1,500 megawatts, or about 15 percent of their total nameplate capacity. Put another way, wind energy was able to provide only about 2.2 percent of the total power demand even though the installed capacity of Texas’s wind turbines theoretically equals nearly 15 percent of peak demand. This was no anomaly. On four days in August 2010, when electricity demand set records, wind energy was able to contribute just 1, 2, 1, and 1 percent, respectively, of total demand.
Over the past few years, about $17 billion has been spent installing wind turbines in Texas. Another $8 billion has been allocated for transmission lines to carry the electricity generated by the turbines to distant cities. And now, Texas ratepayers are on the hook for much of that $25 billion, even though they can’t count on the wind to keep their air conditioners running when temperatures soar.
That $25 billion could have been used to build about 5,000 megawatts of highly reliable nuclear generation capacity, or as much as 25,000 megawatts of natural-gas-fired capacity, all of which could have been reliably put to work during the hottest days of summer.
The wind-energy lobby has been masterly at garnering huge subsidies and mandates by claiming that its product is a “green” alternative to conventional electricity. But the hype has obscured a dirty little secret: When power demand is highest, wind energy’s output is generally low. The reverse is also true: Wind-energy production is usually highest during the middle of the night, when electricity use is lowest.
The incurable intermittency and extreme variability of wind energy requires utilities and grid operators to continue relying on conventional sources of generation like coal, natural gas, and nuclear fuel. Nevertheless, 29 states, plus the District of Columbia, now have renewable-energy mandates. Those expensive mandates cannot be met with solar energy, which, despite enormous growth in recent years, still remains a tiny player in the renewable sector. If policymakers want to meet those mandates, landowners and citizens will have to learn to live with sprawling forests of noisy, 45-story-tall wind turbines.
The main motive for installing all those turbines is that they are supposed to help reduce carbon-dioxide emissions, which, in turn, is supposed to help prevent global temperature increases. But it’s already hot – really hot – in Texas and other parts of the southern United States. And that leads to an obvious question: If the global-warming catastrophists are right, and it’s going to get even hotter, then why the heck are we putting up wind turbines that barely work when it’s hot?
This article is the work of the source indicated. Any opinions expressed in it are not necessarily those of National Wind Watch.
The copyright of this article resides with the author or publisher indicated. As part of its noncommercial educational effort to present the environmental, social, scientific, and economic issues of large-scale wind power development to a global audience seeking such information, National Wind Watch endeavors to observe “fair use” as provided for in section 107 of U.S. Copyright Law and similar “fair dealing” provisions of the copyright laws of other nations. Send requests to excerpt, general inquiries, and comments via e-mail.
| Wind Watch relies entirely on User Funding |
 (via Stripe) |
 (via Paypal) |
Share:

